반응형
이진영상이란?
- 영상이 흑(0)과 백(1) 과 같이 두 가지 값만을 가진 영상을 말한다.
- 두 구간을 가르는 임계값(Threshold) T를 취해 임계값 보다 큰 화소는 백(1)으로 취하고, 그렇지 않은 화소는 흑(0)으로 바꾼다.
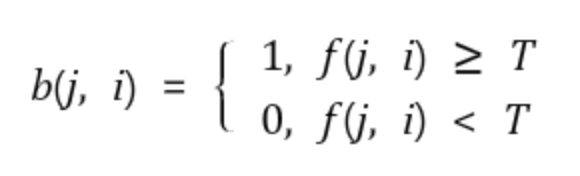
이진화 알고리즘
import cv2
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline# 비교를 위한 가시화 함수
def plot_img(images, titles):
fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows = 1, ncols = len(images), figsize = (15, 15))
for i, p in enumerate(images):
axs[i].imshow(p, 'gray')
axs[i].set_title(titles[i])
plt.show()# 이미지 다운로드
!wget https://www.shrednations.com/wp-content/uploads/corporate-espionage.jpg
!wget https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/4b/Image_processing_pre_otsus_algorithm.jpg# 영상 읽기 및 가시화
img1 = cv2.imread('corporate-espionage.jpg', 0)
plt.imshow(img1, 'gray')
plt.show()
height1, width1 = img1.shape
print(width1, height1)
이진화 알고리즘 직접 구현
binary_img1 = numpy.zeros(img1.shape, numpy.uint8)
threshold = 128
for i in range(height1):
for j in range(width1):
if img1[i][j]>threshold:
binary_img1[i][j] = 255
else:
binary_img1[i][j] = 0
images = [img1, binary_img1]
titles = ['Original image', 'Hard_threshold']
plot_img(images, titles)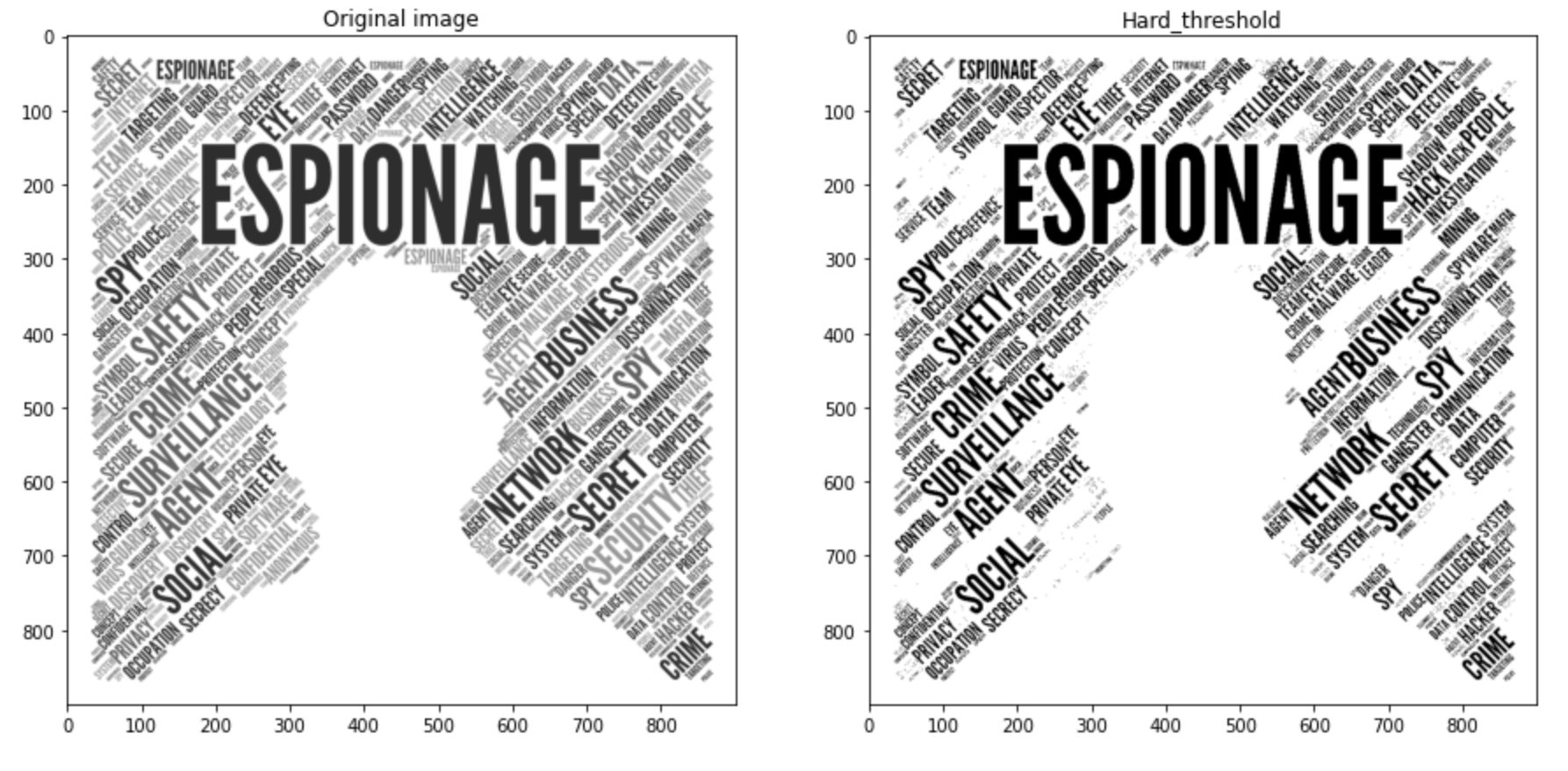
OpenCV 이진화 라이브러리
ret, img_binary1 = cv2.threshold(img1, 128, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# Plot the images
images = [img1, img_binary1]
titles = ['Original image', 'THRESH_BINARY']
plot_img(images, titles)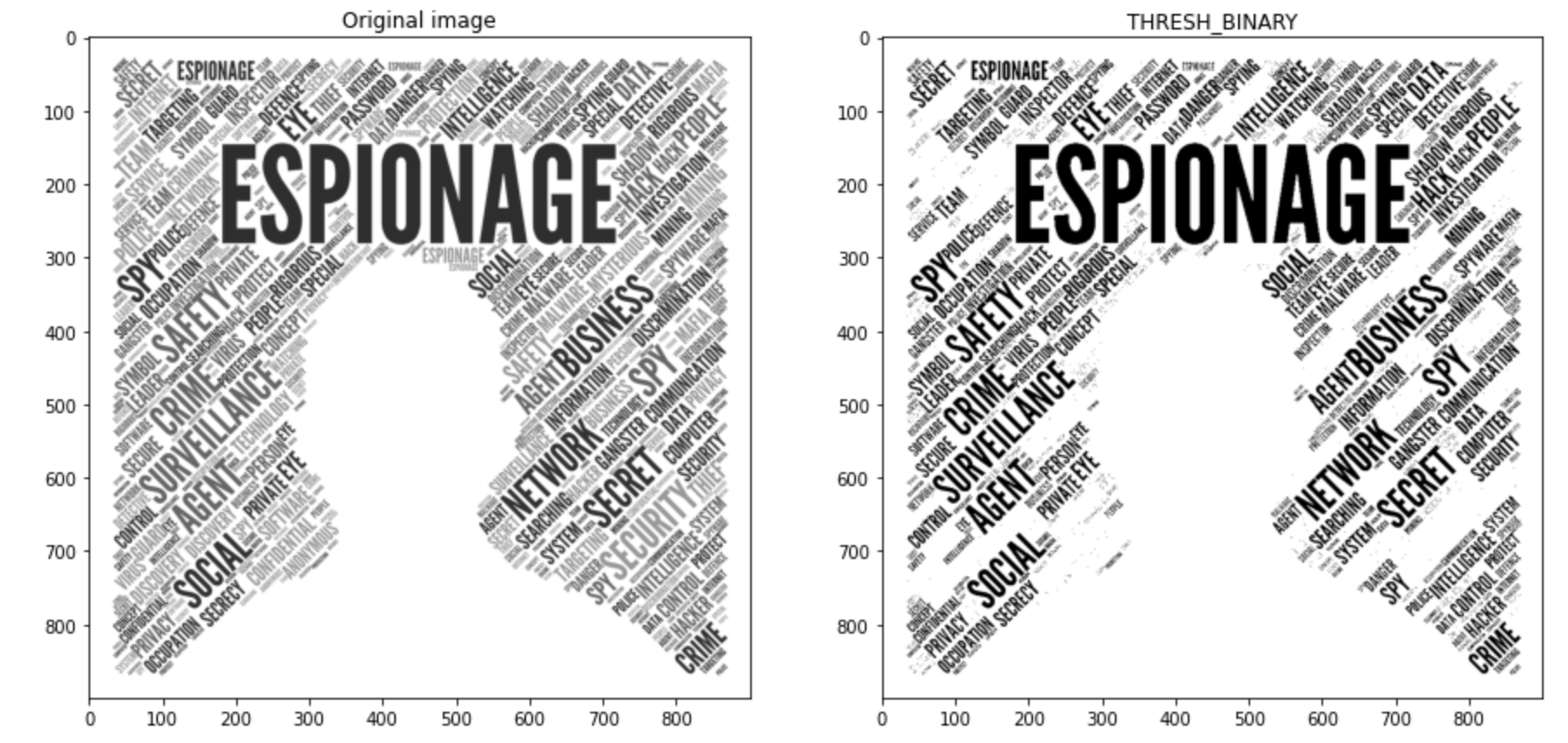
오츄 알고리즘을 통한 이진화
오츄 알고리즘
- 임계값 T를 기준으로 화소를 두 집합으로 나누었을 떄, 각 집합의 명암 분포가 균일할 수록 좋다는 점에 착안해 균일 성이 클 수록 T에게 높은 점수를 준다.
- 균일성은 그룹의 분산으로 측정하고 분산이 작을 수록 균일성이 높다.
- 가능한 T에 대해 점수를 계산한 후 가장 좋은 T를 최종 임계값으로 취한다. 일종의 최적화 알고리즘이다.
# 영상 읽기 및 가시화
img2 = cv2.imread('Image_processing_pre_otsus_algorithm.jpg', 0)
plt.imshow(img2, 'gray')
plt.show()
hegith2, width2 = img2.shape
print(width2, height2)
오츄 알고리즘 직접 구현
hist = cv2.calcHist([img2],[0],None,[256],[0,256])
hist_norm = hist.ravel()/hist.max()
CDF = hist_norm.cumsum()#initialization
bins = numpy.arange(256)
fn_min = numpy.inf
thresh = -1#Otsu algorithm operation
for i in range(1,256):
p1,p2 = numpy.hsplit(hist_norm,[i]) # probabilities
q1,q2 = CDF[i],CDF[255]-CDF[i] # cum sum of classes
if q1 == 0:
q1 = 0.00000001
if q2 == 0:
q2 = 0.00000001
b1,b2 = numpy.hsplit(bins,[i]) # weights
# finding means and variances
m1,m2 = numpy.sum(p1*b1)/q1, numpy.sum(p2*b2)/q2
v1,v2 = numpy.sum(((b1-m1)**2)*p1)/q1,numpy.sum(((b2-m2)**2)*p2)/q2
# calculates the minimization function
fn = v1*q1 + v2*q2
if fn < fn_min:
fn_min = fn
thresh = i
thresh153
otsu_img = numpy.zeros(img2.shape, numpy.uint8)
for i in range(img2.shape[0]):
for j in range(img2.shape[1]):
if img2[i][j]<thresh:
otsu_img[i][j] = 0
else:
otsu_img[i][j] = 255;
images = [img2, otsu_img]
titles = ['Original image', 'THRESH_BINARY']
plot_img(images, titles)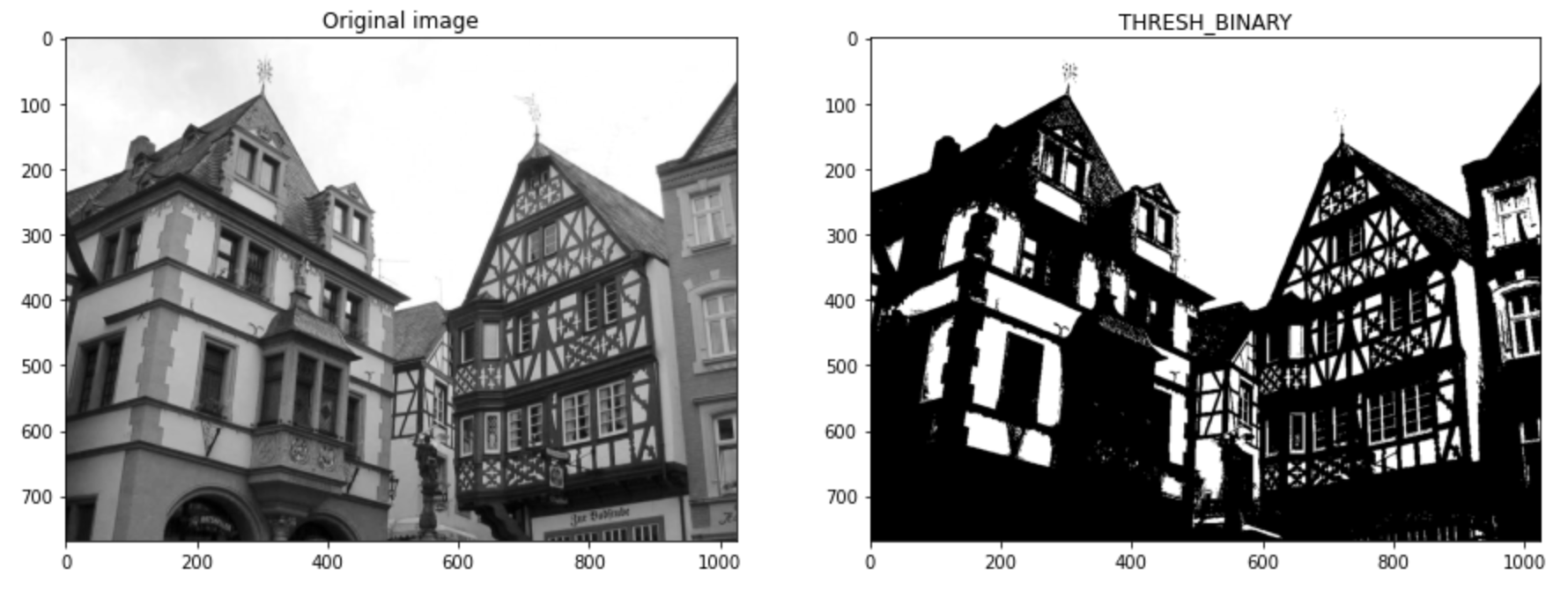
OpenCV 오츄 라이브러리
ret, otsu = cv2.threshold(img2,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
print( "{} {}".format(thresh,ret) )153 152.0
참고
- https://n-square.tistory.com/113
- [컴퓨터비전] 국민대학교 윤상민 교수님 수업 참고
반응형
'Computer vision' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Computer vision] 이진화 영상 팽창(dilation), 침식(erosion), 열기(open), 닫기(close) (0) | 2021.12.03 |
|---|---|
| [Computer vision] 이진영상 라벨링하기 / 4연결성(4-neighbors), 8연결성(8-neighbors) (0) | 2021.10.27 |
| [Computer vision] 라플라시안 연산자 (Laplacian Operator) (0) | 2021.09.30 |
| [Computer vision] 선형 필터(Linear Filter) / 박스 필터(Box Filter), 가우시안 필터(Gaussian Filter) (0) | 2021.09.23 |
| [Computer vision] 컨볼루션 Convolution이란? (0) | 2021.09.23 |



